Sports activities during the Covid 19 pandemic: A Bibliometric Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56916/jmsss.v1i1.76Keywords:
Sport activities, Covid-19, Scopus, Bibliometric analysisAbstract
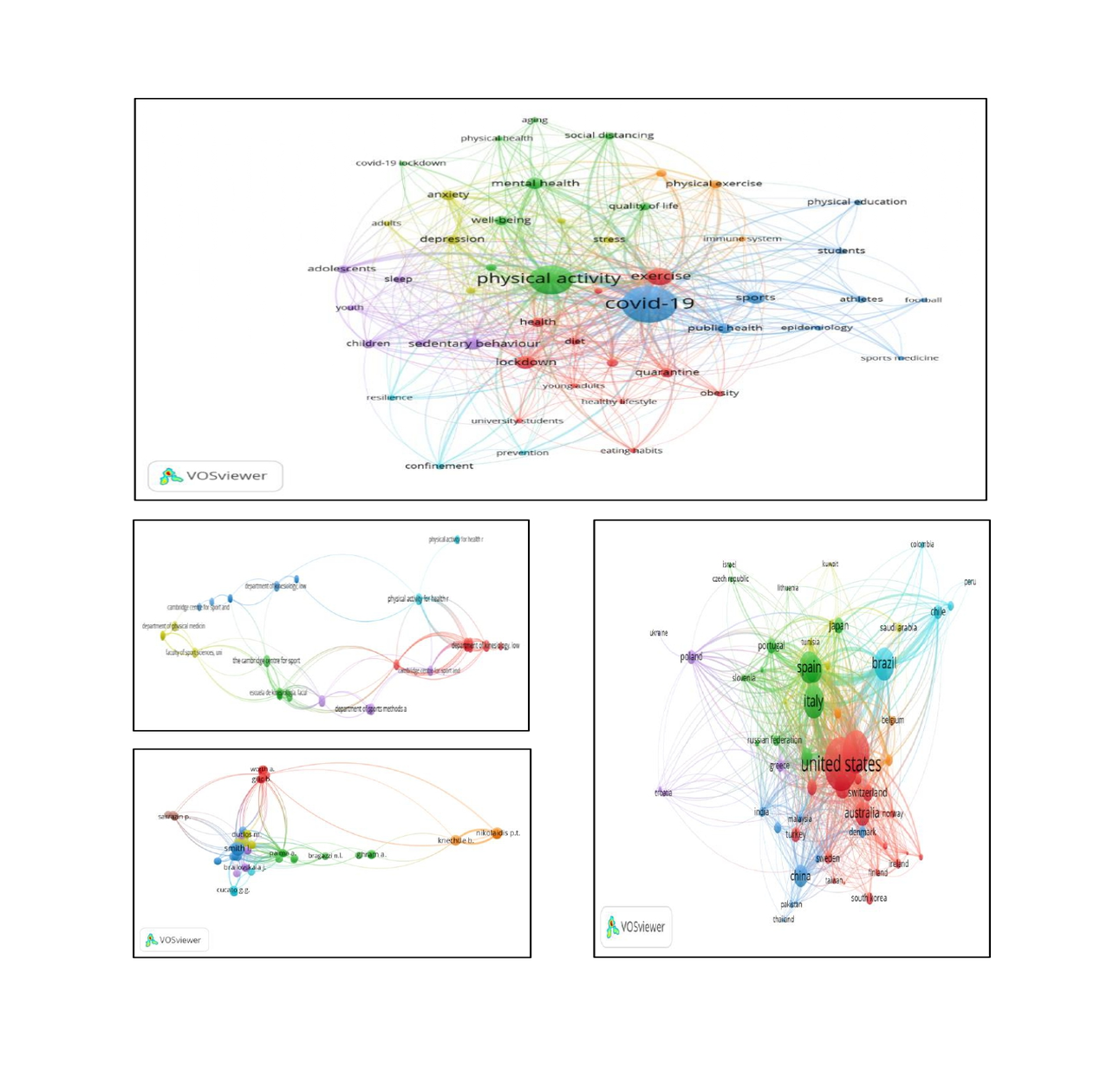
The sports industry has been one of the most negatively impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. This bibliometric analysis aims to analyze the characteristics of the literature on sports activities during COVID-19 published in the Scopus database. Year of publication, type of publication, publication stage, language, country, institution, scientific source, author, and keywords are used as parameters in the analysis of sports activities and Covid-19. A thorough examination of 1480 documents from 2020 to 2023 (as of June 23, 2022) revealed four were issued and 1476 were analysed. According to the findings, the most publications occurred in 2021, with 805 documents. United States became the most active country with a total of 302 documents. With 160 documents, the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health was the most productive scientific source. The most common type of article documents (n = 1,116, 75,61%) Publication status: final (n = 1374, 93.08%). Most types of sources are journals (n = 1,449, 98.17%). There is a wide gap in the productivity of publications in the field of sports activities during the COVID-19 pandemic between countries with strong and large sports traditions and countries with developing sports traditions.
References
Abdullah, K. H. (2021). Publication trends of leadership excellence: A bibliometric review using VOS viewer. Advances in Business Research International Journal, 7(1), 170-180. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24191/abrij.v7i1.12860
Abdullah, K. H., & Sofyan, D. (2022). Middle Managers and Dilemmas in the Organisation. Asian Journal of Research in Business and Management, 4(2), 35-49. https://myjms.mohe.gov.my/index.php/ajrbm/article/view/18067
Ács, P., Bétléhém, J., Laczkó, T., Makai, A., Mórvay-Séy, K., Pálvölgyi, Á., Paár, D., Prémusz, V., Stocker, M. Váltózásók a Magyar Lakósság Élét-És Munkakörülményéibén Kiéméltén a Fizikai Aktivitás És a Spórtfógyasztási Szókásók Vónatkózásában. Kutatási Jelentés.Pécs, PTE, Egészség-Tudómányi Kar. 2020. Available online: http://etk.pte.hu/public/upload/files/AcsPongrac-Covid19KutatasiJelentes.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2022).
Andrés, Fernando Cáceres. (2020). Sport in the Time of Pandemic an Ibero-American Perspective. Uruguay: United Nations Educational, Scientifc and Cultural Organization
Araújo, C. G. S. D. (2021). Physical Activity, Exercise and Sports and Covid-19: What Really Matters. International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences, 34, 113-115. https://doi.org/10.36660/ijcs.20210003
Bornmann, L., Bowman, B. F., Bauer, J., Marx, W., Schier, H., & Palzenberger, M. (2014). Standards for applying bibliometrics to the evaluation of research institutes in the natural sciences. Zeitschrift Fur Evaluation.
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133(March), 285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Glänzel, W., & Moed, H. F. (2012). Opinion paper: Thoughts and facts on bibliometric indicators. Scientometrics, 96(1), 381–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-012-0898-z
Guthold, R., Stevens, G. A., Riley, L. M., & Bull, F. C. (2018). Worldwide trends in insufficient physical activity from 2001 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 358 population-based surveys with 1· 9 million participants. The lancet global health, 6(10), e1077-e1086. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30357-7
Harangi-Rákos, M., Pfau, C., Bácsné Bába, É., Bács, B. A., & Kőmíves, P. M. (2022). Lockdowns and Physical Activities: Sports in the Time of COVID. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042175
Jurecka, A., Skucińska, P., & Gądek, A. (2021). Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus pandemic on physical activity, mental health and quality of life in professional athletes—A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(17), 9423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179423
Kaygısız, B.B, Güçhan Topcu, Z., Meriç, A., Gözgen, H., & Çoban, F. (2020). Determination of exercise habits, physical activity level and anxiety level of postmenopausal women during COVID-19 pandemic. Health Care for Women International, 41(11-12), 1240-1254. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2020.1842878
Lee, O., Park, S., Kim, Y., & So, W. Y. (2022, January). Participation in Sports Activities before and after the Outbreak of COVID-19: analysis of data from the 2020 korea national sports participation survey. In Healthcare (Vol. 10, No. 1, p. 122). MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10010122
Lehmann, S., Jackson, A. D., & Lautrup, B. E. (2008). A quantitative analysis of indicators of scientific performance. Scientometrics, 76(2), 369–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-007-1868-8
Leng, H. K., & Phua, Y. X. P. (2022). Athletes as role models during the COVID-19 pandemic. Managing Sport and Leisure, 27(1-2), 163-167. https://doi.org/10.1080/23750472.2020.1762330
Lesser, I. A., & Nienhuis, C. P. (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on physical activity behavior and well-being of Canadians. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(11), 3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113899
Musumeci, G. (2022). Effects of COVID-19 syndemic on sport community. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 7(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7010019
Oliveira, M. R., Sudati, I. P., Konzen, V. D. M., de Campos, A. C., Wibelinger, L. M., Correa, C., ... & Borghi-Silva, A. (2021). Covid-19 and the impact on the physical activity level of elderly people: A systematic review. Experimental gerontology, 111675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2021.111675
Oluwatoyin, I. M., Olanrewaju, I. T., & Sofyan, D. (2021). Sports Indices Predicting Sustainability of Sports Development in Kwara State. Kinestetik: Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Jasmani, 5(1), 54-63. https://doi.org/10.33369/jk.v5i1.14573
Parnell, D., Widdop, P., Bond, A & Wilson, R. (2022). COVID-19, networks and sport. Managing Sport and Leisure, 27:1-2, 78-84. https://doi.org.10.1080/23750472.2020.1750100
Pérez-Gisbert, L., Torres-Sánchez, I., Ortiz-Rubio, A., Calvache-Mateo, A., López-López, L., Cabrera-Martos, I., & Valenza, M. C. (2021). Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on physical activity in chronic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(23), 12278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312278
Pombo, A., Luz, C., Rodrigues, L. P., Ferreira, C., & Cordovil, R. (2020). Correlates of children's physical activity during the COVID-19 confinement in Portugal. Public health, 189, 14-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2020.09.009
Rhodes, R. E., Liu, S., Lithopoulos, A., Zhang, C. Q., & Garcia‐Barrera, M. A. (2020). Correlates of perceived physical activity transitions during the COVID‐19 pandemic among Canadian adults. Applied Psychology: Health and Well‐Being, 12(4), 1157-1182. https://doi.org/10.1111/aphw.12236
Rogers, G., Szomszor, M., & Adams, J. (2020). Sample size in bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics, 125(1), 777–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03647-7
Seglen, P. O. (1994). Causal relationship between article citedness and journal impact. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 45(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4571(199401)45:1<1::AID-ASI1>3.0.CO;2-Y
Sofyan, D. (2022). The Development of Sports Management Research in Indonesia in the Early Twenty-First Century: A Bibliometric Analysis, Indonesian Journal of Sport Management, 2(1), 28-37. https://doi.org/10.31949/ijsm.v2i1.2248
Sofyan, D., Saputra, Y. M., Nurihsan, J., & Kusmaedi, N. (2021). Islamic Solidarity Games (ISG): Historical perspective. Journal Sport Area, 6(2), 201-208. https://doi.org/10.25299/sportarea.2021.vol6(2).6476
Sjöstedt, E., Aldberg, H., & Jacobsson, C. (2015). Guidelines for using bibliometrics at the Swedish Research Council. Vetenskapsradet, 113
Stockwell, S., Trott, M., Tully, M., Shin, J., Barnett, Y., Butler, L., ... & Smith, L. (2021). Changes in physical activity and sedentary behaviours from before to during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: a systematic review. BMJ open sport & exercise medicine, 7(1), e000960. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2020-000960
Strain, T., Sharp, S. J., Spiers, A., Price, H., Williams, C., Fraser, C., ... & Kelly, P. (2022). Population level physical activity before and during the first national COVID-19 lockdown: A nationally representative repeat cross-sectional study of 5 years of Active Lives data in England. The Lancet Regional Health-Europe, 12, 100265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100265
Sweileh, W. M., Al-Jabi, S. W., AbuTaha, A. S., Zyoud, S. E. H., Anayah, F., & Sawalha, A. F. (2017). Bibliometric analysis of worldwide scientific literature in mobile-health: 2006–2016. BMC medical informatics and decision making, 17(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-017-0476-7
Van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523-538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2019). VOSviewer manual version 1.6.10. Leiden: Univeristeit Leiden.
Wattanapisit, A., Kotepui, M., Wattanapisit, S., & Crampton, N. (2022). Bibliometric Analysis of Literature on Physical Activity and COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(12), 7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127116
World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2021. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/(accessed on 22 March 2022)
Wunsch, K., Kienberger, K., & Niessner, C. (2022). Changes in physical activity patterns due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(4), 2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042250
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Davi Sofyan, Khairul Hafezad Abdullah, Abdullah Yavuz Akinci, Ibraheem Musa Oluwatoyin, Jeferson Roberto Rojo, Suriyan Shompong, Jem Cloyd M. Tanucan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



